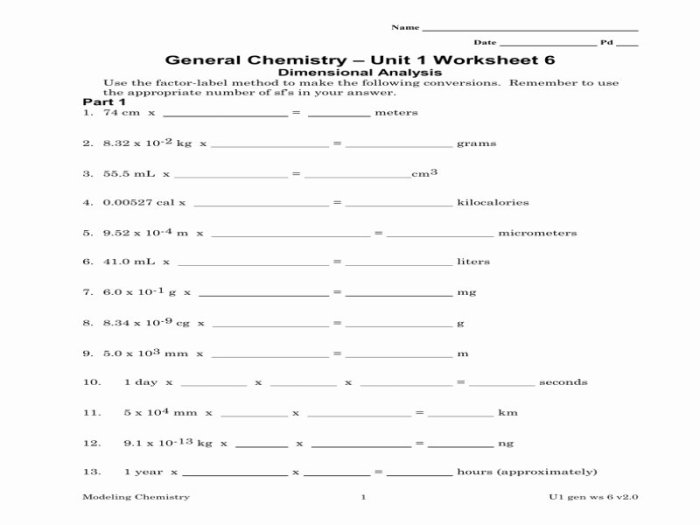
Chemistry unit 1 worksheet 6 dimensional analysis – Embark on a journey into the realm of Chemistry Unit 1 Worksheet 6: Dimensional Analysis, where we delve into the art of manipulating units to solve complex chemistry problems. This essential skill empowers chemists to navigate the intricacies of chemical calculations with precision and confidence.
Through a comprehensive exploration of dimensional analysis, we uncover its fundamental concepts, unravel the intricacies of unit conversion, and tackle a diverse array of dimensional analysis problems. By harnessing the power of this technique, we unlock the ability to solve real-world chemistry problems and make meaningful contributions to scientific discoveries.
Dimensional Analysis in Chemistry
Dimensional analysis is a powerful tool used in chemistry to convert units between different systems and to solve problems involving quantities with different units.
Explain the concept of dimensional analysis.
Dimensional analysis is based on the principle that an equation must be dimensionally balanced, meaning that the units of the quantities on both sides of the equation must be the same.
Provide examples of dimensional analysis in chemistry.
Examples of dimensional analysis in chemistry include:
- Converting units of temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Converting units of volume from liters to milliliters
- Converting units of mass from grams to kilograms
Discuss the importance of dimensional analysis in chemistry.
Dimensional analysis is important in chemistry because it allows scientists to:
- Ensure that their calculations are correct
- Compare data from different sources
- Solve problems involving quantities with different units
Unit Conversion
Explain how to convert units using dimensional analysis., Chemistry unit 1 worksheet 6 dimensional analysis
To convert units using dimensional analysis, you need to:
- Identify the quantity you want to convert.
- Find the conversion factor that relates the original unit to the desired unit.
- Multiply the original quantity by the conversion factor.
Provide a step-by-step guide to unit conversion.
Here is a step-by-step guide to unit conversion:
- Write down the original quantity and unit.
- Identify the desired unit.
- Find the conversion factor that relates the original unit to the desired unit.
- Multiply the original quantity by the conversion factor.
- Check your answer to make sure that it has the correct units.
Share tips for avoiding common mistakes in unit conversion.
Here are some tips for avoiding common mistakes in unit conversion:
- Make sure that you are using the correct conversion factor.
- Be careful not to cancel out units that should not be canceled out.
- Check your answer to make sure that it has the correct units.
Dimensional Analysis Problems
Design a variety of dimensional analysis problems.
Here are some examples of dimensional analysis problems:
- A bottle of water contains 1 liter of water. How many milliliters of water are in the bottle?
- A car travels 100 kilometers in 1 hour. What is the car’s speed in meters per second?
- A person weighs 150 pounds. What is the person’s weight in kilograms?
Organize the problems into different levels of difficulty.
The problems can be organized into different levels of difficulty, such as:
- Easy: Problems that involve converting between units of the same type (e.g., liters to milliliters)
- Medium: Problems that involve converting between units of different types (e.g., kilometers to meters per second)
- Hard: Problems that involve multiple conversions (e.g., converting pounds to kilograms and then kilograms to grams)
Create an answer key for the problems.
Here is an answer key for the problems:
- 1 liter = 1000 milliliters
- 100 kilometers / 1 hour = 27.78 meters per second
- 150 pounds = 68.04 kilograms
Applications of Dimensional Analysis: Chemistry Unit 1 Worksheet 6 Dimensional Analysis
Elaborate on the applications of dimensional analysis in chemistry.
Dimensional analysis has a wide range of applications in chemistry, including:
- Converting units between different systems
- Solving problems involving quantities with different units
- Checking the accuracy of calculations
Discuss how dimensional analysis can be used to solve real-world problems.
Dimensional analysis can be used to solve a variety of real-world problems, such as:
- Calculating the amount of fuel needed to drive a car a certain distance
- Determining the concentration of a solution
- Predicting the products of a chemical reaction
Provide examples of how dimensional analysis has been used in scientific discoveries.
Dimensional analysis has been used in a number of scientific discoveries, including:
- The discovery of the atomic mass of oxygen
- The development of the periodic table
- The formulation of the laws of thermodynamics
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of dimensional analysis in chemistry?
Dimensional analysis is a technique used to ensure that the units of measurement in a calculation are consistent and that the final answer is expressed in the correct units.
How can I avoid common mistakes in unit conversion?
To avoid common mistakes in unit conversion, it is important to pay attention to the units of measurement in each step of the calculation and to use the correct conversion factors.
What are some real-world applications of dimensional analysis?
Dimensional analysis is used in a variety of real-world applications, such as converting units of measurement in recipes, calculating the dosage of medications, and designing chemical experiments.